|
||||||||||||||||||||||
![Home - Air Power Australia Website [Click for more ...]](APA/APA-Title-Main.png) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
![Sukhoi PAK-FA and Flanker Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/flanker.png) |
![F-35 Joint Strike Fighter Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/jsf.png) |
![Weapons Technology Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/weps.png) |
![News and Media Related Material Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/media.png) |
|||||||||||||||||||
![Surface to Air Missile Systems / Integrated Air Defence Systems Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/sams-iads.png) |
![Ballistic Missiles and Missile Defence Page [Click for more ...]](APA/msls-bmd.png) |
![Air Power and National Military Strategy Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/strategy.png) |
![Military Aviation Historical Topics Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/history.png)
|
![Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance and Network Centric Warfare Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/isr-ncw.png) |
![Information Warfare / Operations and Electronic Warfare Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/iw.png) |
![Systems and Basic Technology Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/technology.png) |
![Related Links Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/links.png) |
|||||||||||||||
![Homepage of Australia's First Online Journal Covering Air Power Issues (ISSN 1832-2433) [Click for more ...]](APA/apa-analyses.png) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last Updated: Mon Jan 27 11:18:09 UTC 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
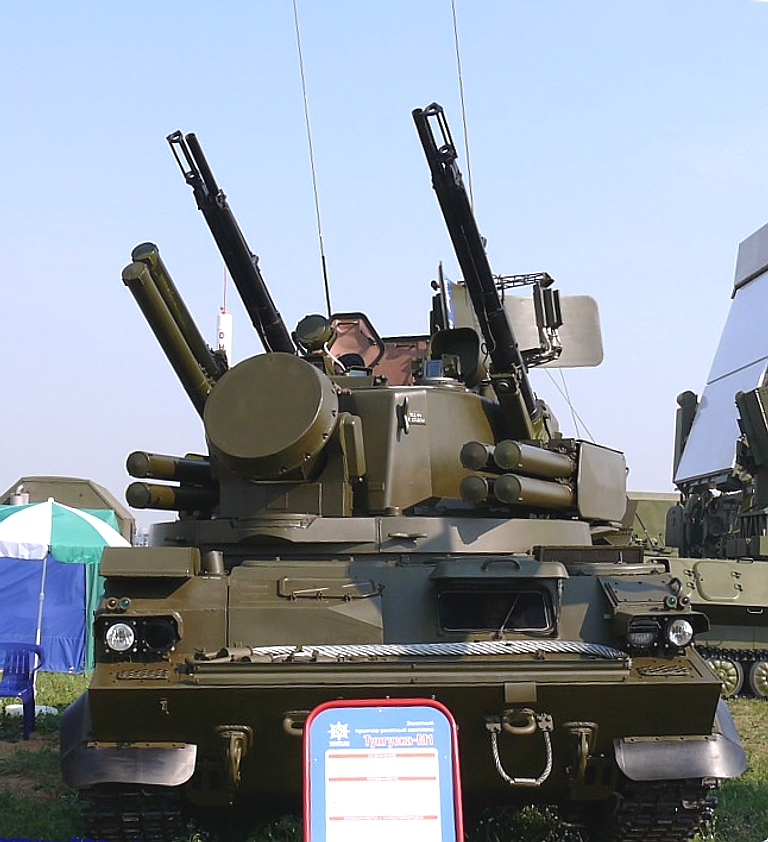
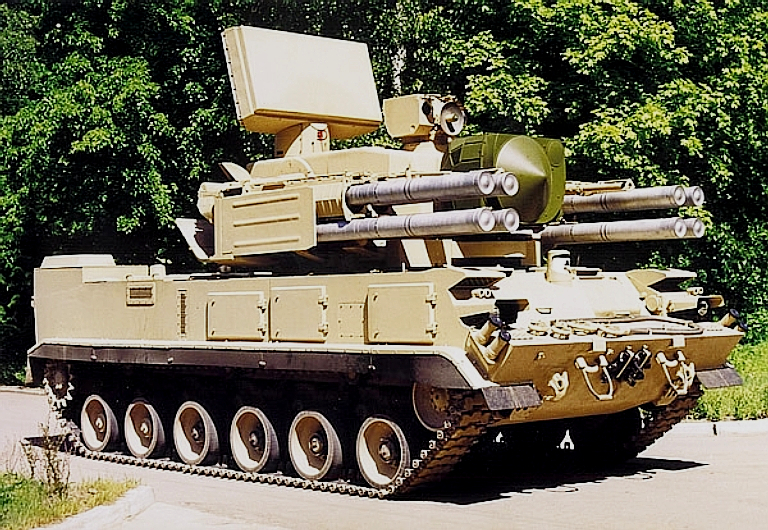
KBP
2K22/2K22M/M1
Tunguska
SA-19
Grison
/
96K6 Pantsir S1 / SA-22 Greyhound SPAAGM Cамоходный Зенитный Ракетно-Пушечный Комплекс КБП 2К22М/М1 Тунгуска-М/М1 / 96К6 Панцирь-С1 Technical Report APA-TR-2009-0703 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| by
Dr
Carlo
Kopp, AFAIAA,
SMIEEE,
PEng July 2009 Updated August, 2010 Updated May, 2011 Updated April, 2012 Text © 2009-2012 Carlo Kopp  |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
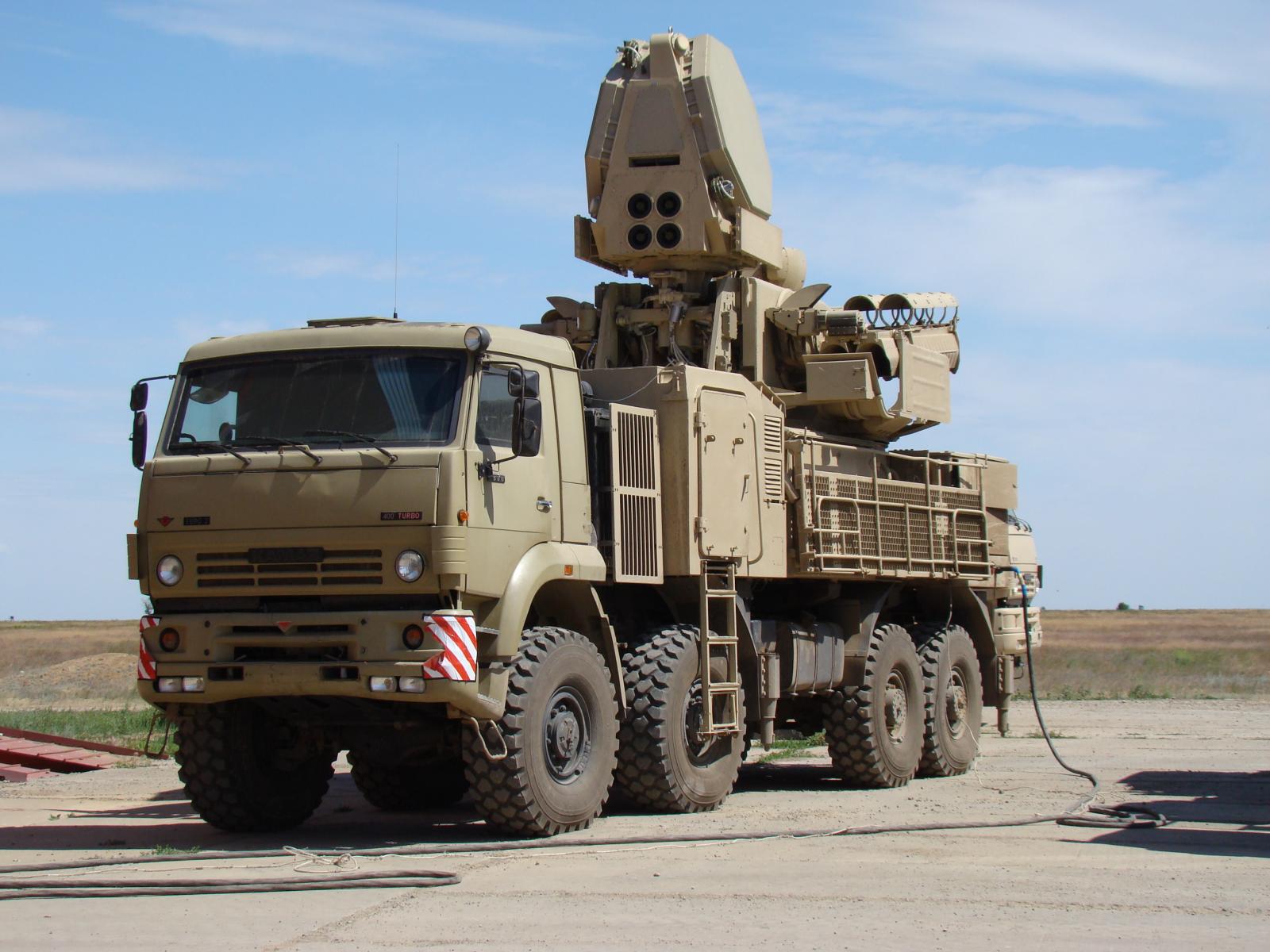
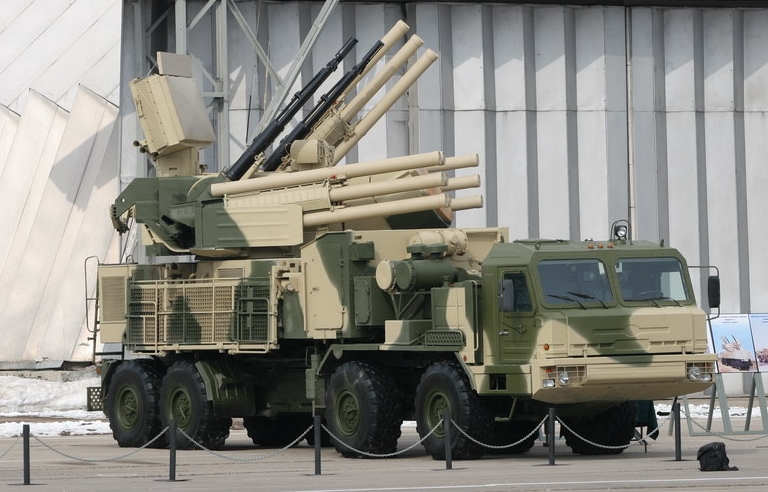 Fully
deployed
72V6
SPAAGM
prototype
on
BAZ-6909
chassis.
This
variant
incorporates a new VNIIRT designed 1RS2-1E agile
beam
phased array engagement radar. The primary design aim for
this system was the interception of PGMs, especially the AGM-88 HARM
and GBUs (Sergei Kuznetsov
via Strizhi.ru).
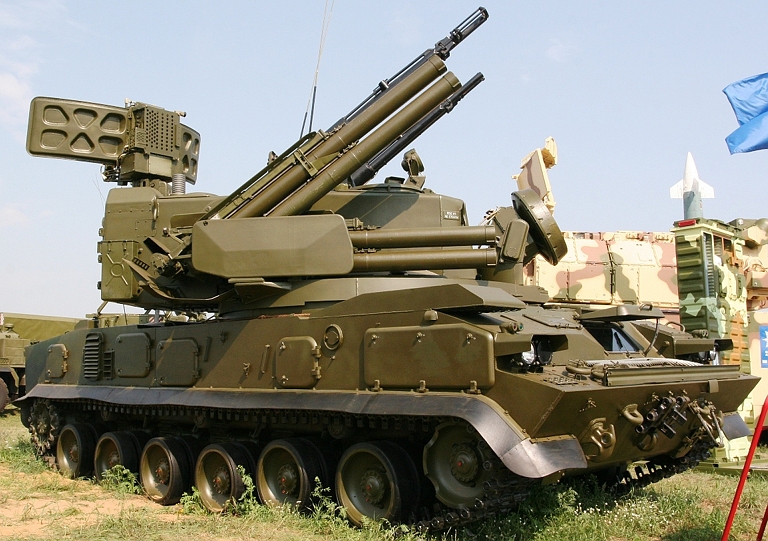
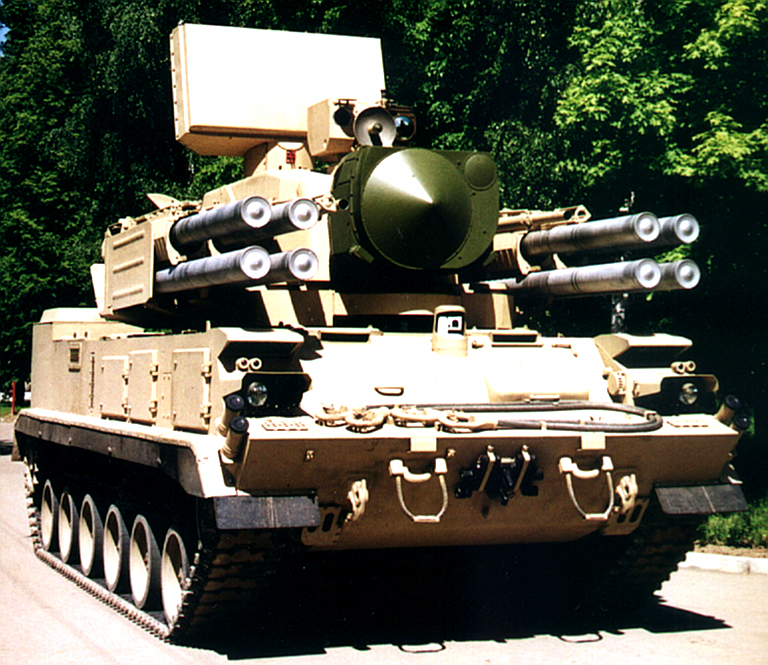
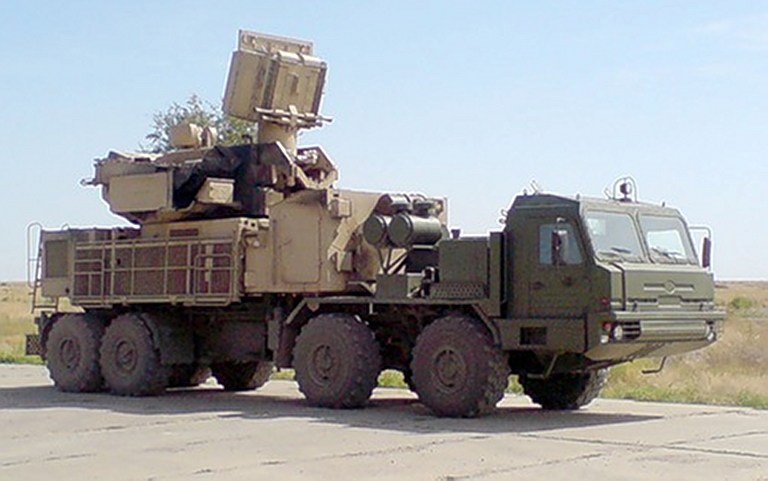
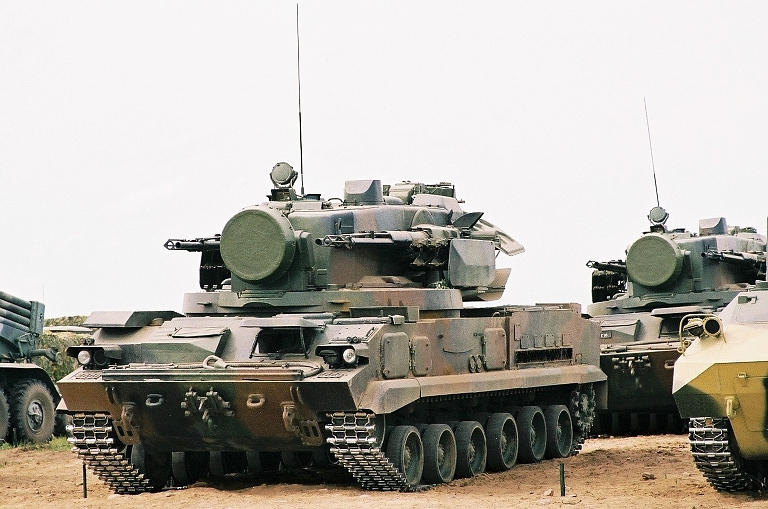 2S6M Tunguska M at the Berezina 2002
exercise. Most of the Soviet inventory of these capable SPAAGMs ended
up in the Russian, Ukrainian and Belarus Army inventories. The most
notable export client has been India (© Miroslav
Gyűrösi).
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Background
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
  |
Left: CONOPS
diagram for the Pantsir S system. Right: early
Pantsir S demonstrator on the 8 x 8 Ural-5323.4 vehicle.
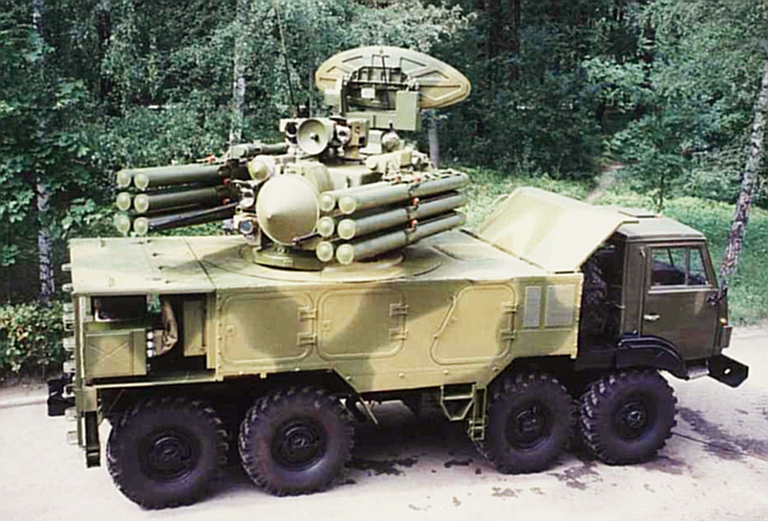

Early Pantsir S1 / SA-22
demonstrator on the 8 x 8 Ural-5323.4 vehicle. Note the configuration
of the search and engagement radar
antennas. This design used the earlier 9M335 missile round and the
1L36-1 Roman engagement radar (KBP).
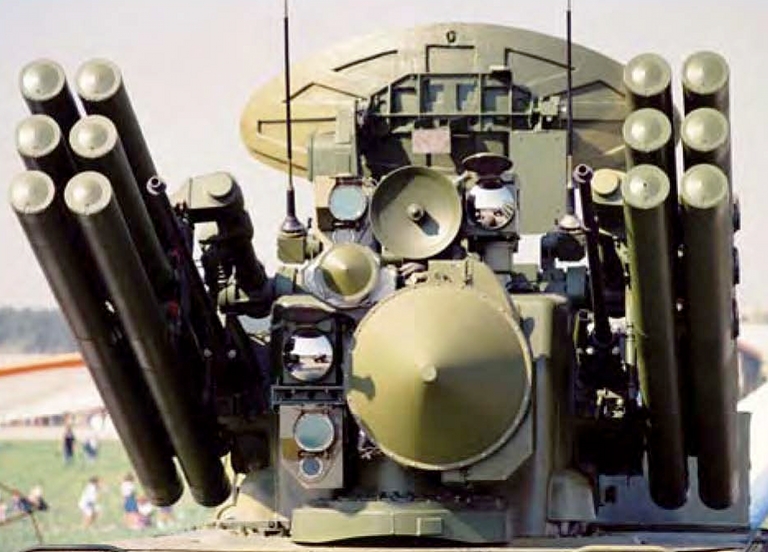


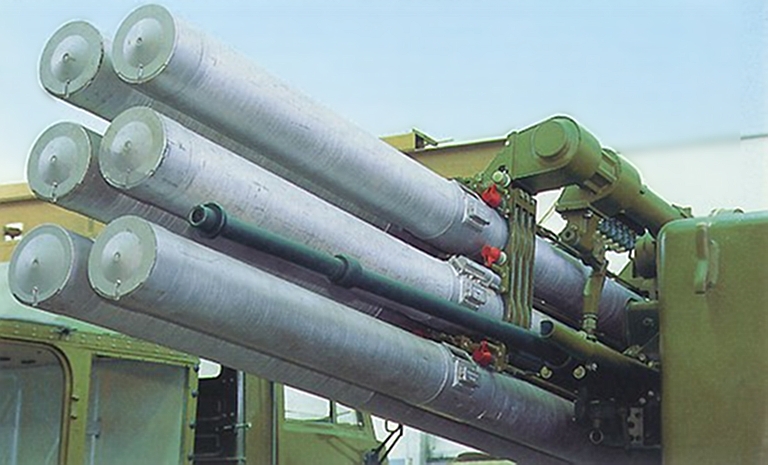
Above: Detail of Pantsir S demonstrator turret, showing the dual band Phazotron 1L36 Roman engagement radar and early Russian designed electro-optical suite, early 9M335 missile launchers and early 30 mm guns (image © Miroslav Gyűrösi); Below: detail of 9M335 missile launch tubes and 30 mm gun (via Russkaya Sila).


A configuration of the Pantsir S1 which remains on offer uses the 8 x 8 MZKT-7930 chassis, providing much better cross country mobility than the lighter KAMAZ chassis, at a cost. It is not known whether this image using a stretched chassis represents a mockup or prototype (KBP).
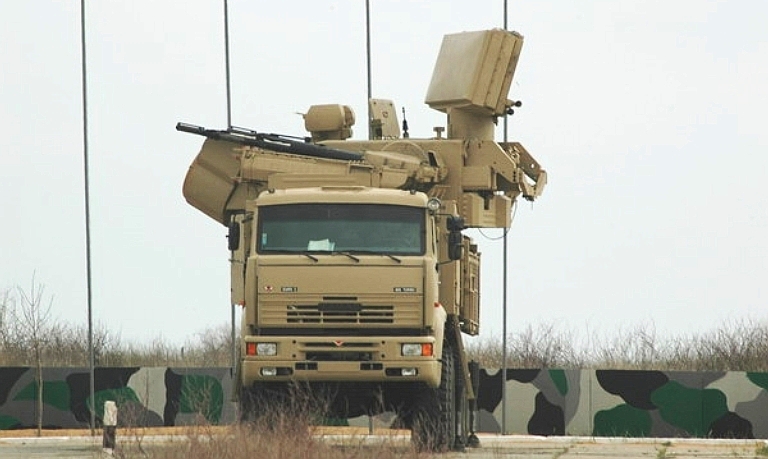

The production
Pantsir S1 configuration at MAKS-2007, carried by an 8 x 8 KAMAZ-6560
chassis.
The tracked chassis used with the 2S6 Tunguska was not well suited to V-PVO needs, as it had a slower road speed than the wheeled S-300P SAM systems, was less reliable and more expensive to maintain than a wheeled system, and the chassis dimensions limited the number of ready rounds and reloads, and carried 30 mm gun ammunition. The light tank style of tracked chassis was well hardened, in excess of V-PVO needs, being built for a battlefield environment. The V-PVO needed a design with more firepower, faster transit speeds to permit co-deployment with S-300P series SAM batteries, and a low procurement and operating cost. This dictated a wheeled host vehicle, much larger than the light tank sized tracked chassis of 2S6 Tunguska series, and new turret design to accommodate more launch tubes and newer and larger radar equipment.
The first prototype of the Pantsir S was displayed in 1995, using an enlarged derivative of the Tunguska's 9K311 missile, the 9K335. Twelve of these missiles were carried in elevating launch tubes. A pair of liquid cooled 2A72 30 mm guns were used, the 2A72 providing 300 - 450 rds/min, with a 970 m/s muzzle velocity and an effective range of 3,000 - 4,000 metres.
The Pantsir S system was equipped with the NIIR Phazotron 1L36-01 Roman / Hot Shot which used an S-band search component with a folding paraboloid section antenna, and a dual band X/MMW band engagement component, under a characteristic conical radome. Performance requirements included tracking 0.1 m2 targets at 15 km range. Typically two targets could be concurrently engaged using the radar, and two using the adjunct electro-optical tracking system. This radar package was later supplanted by the dual band 1RS-2E Shlem, which remains on offer for some variants.
The system ran into development problems, and limitations such as the inability to fire while on the move were considered unacceptable, resulting in a collapse of funding during this period. KBP continued experimenting with the design, using company funding.
The result of this was a deep redesign of the Pantsir S, discarding more of the legacy components and features inherited from the 2S6 series. In particular, the radar package was completely revised, and the turret redesigned.
VNIIRT were engaged to develop a new PESA technology acquisition radar, the 2L80/2L80E, using a mechanically rotated 1776x940 mm sized 760 kg passive phased array.
During the 2005-2006 period, KBP shifted development effort to a new passive phased array design engagement radar, with the capability to track multiple targets and missiles concurrently.
Several chassis were trialled during the development of the 96K6 Pantsir S1 system. Initially the 8 x 8 Ural-5323.4 was used, powered by a 260 SHP KAMAZ-7406 engine, then the 8 x 8 MZKT-7930 was trialled, with the KAMAZ-6530 used for production systems in Russian, and an EU supplied MAN chassis used for systems supplied to the United Arab Emirates. the GM-352 tracked series, common to the Tunguska, remains on offer, but using a reduced missile loadout.
Production Pantsir S1 systems combine the liquid cooled 2A38M 30 mm automatic cannon system with the high velocity 57E6E two stage CLOS missile, based on the Tunguska's 9M311 series. The revised gun design delivers a rate of fire of 1950-2500 rds / min, with a muzzle velocity of 960 metres/s, and the turret magazine capacity was increased to 1400 rounds.
The 57E6E series SAM is unusual in it class as it is a two stage weapon, designed for exceptionally high acceleration to effect snapshots against fleeting targets such as helicopters. Compared to the earlier 9M311 variants, the higher impulse booster stage pushes the second stage to 1,100 m/s. KBP are marketing the system as a capability to engage and destroy the full spectrum of airborne targets, comprising aircraft, UAVs, cruise missiles, precision guided weapons, ballistic missiles and soft skinned surface targets.
KBP define the basic capabilities of the Pantsir series thus (cite):
- High jamming immunity in intensive ECM environment;
- High survivability in massive employment of HARM-type antiradar missiles;
- A capability of destroying high precision weapons, such as Tomahawk cruise missile, Walleye 2 guided air bomb, Maverick guided missile etc;
- A capability of engaging fixed- and rotary- wing aircraft, RPVs, etc.;
- Effectiveness at any time of night and day, in good and adverse weather;
- High mobility, specifically for protecting motorized and armor units;
- High availability and reliability.
The Pantsir S1 series has been primarily marketed in the road mobile configuration, which is less costly to acquire and maintain, and trades away off-road mobility for much higher 90 km/h road speed.
The Pantsir S1 introduces a number of important improvements over the baseline Pantsir S. The new 57E6 missile replaces the established 9M331 series, this weapon provides 20 km range, 70% more than the 9M331M1, a significantly higher maximum target altitude, challenging many area defence missiles, a larger 20 kg warhead, and more thrust to accelerate the missile to 1,300 m/s in 2 seconds.
 96K6 Pantsir S1 power generator module (KBP). |
The layout of the current Pantsir S1 wheeled configuration is highly modular. The weapon system is packaged in a standard 10 tonne container, with three crew stations in the front module, followed by an ECS module, the turret module, with the power generation package in the aft module. The turret cavity contains the 1,400 round magazine for the guns, weapon system computers, mission recorders and other hardware. |
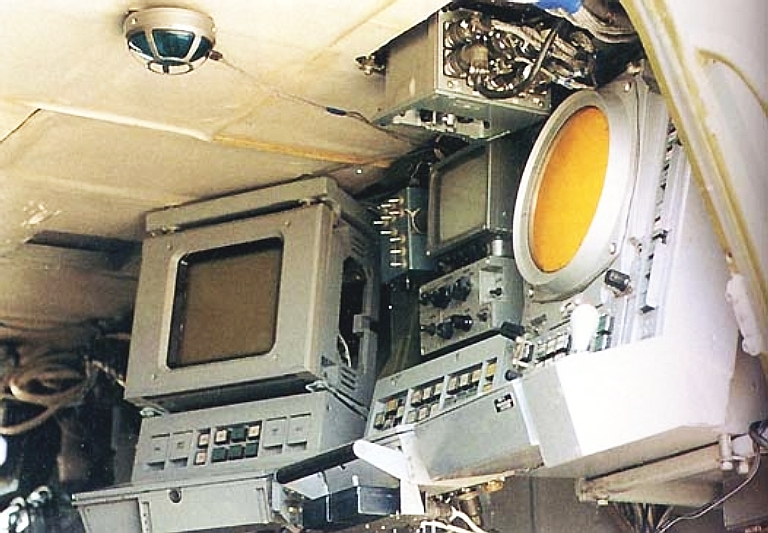

Early
configuration of operator
stations using CRT displays.
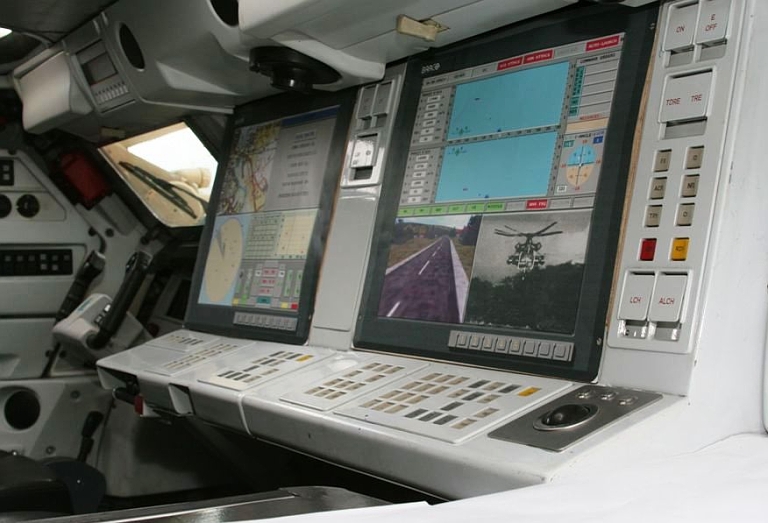

Crew
stations in the recent Pantsir S1E hosted on the GM-352M1E chassis
(image
© Miroslav
Gyűrösi).
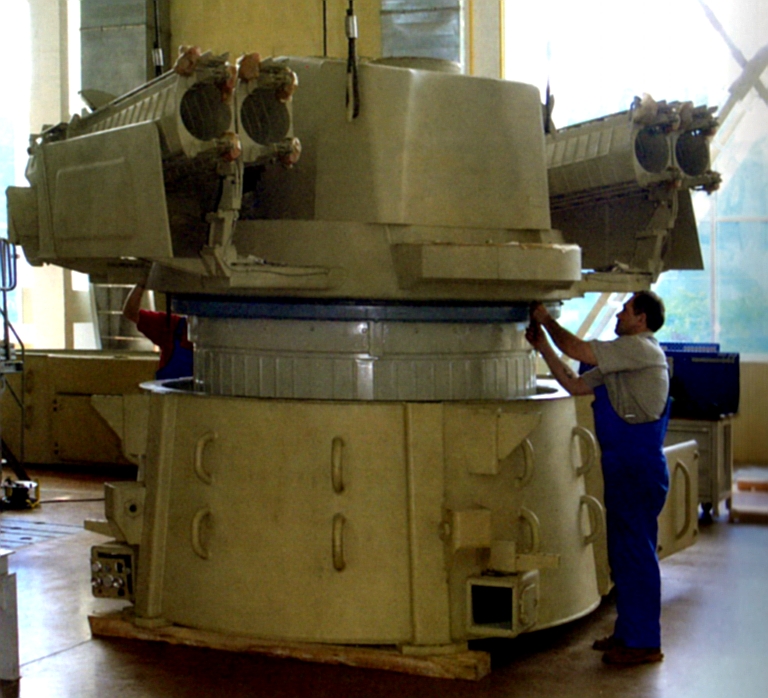
96K6 Pantsir S1 turret assembly being outfitted (KBP).
A more detailed analysis of the Ranzhir Command
Post can be found under Warsaw
Pact
/
Russian
Air
Defence
Command
Posts, and the tracked chassis under Russian
and PLA Point Defence System Vehicles.
96K6 Pantsir S1 turret assembly being outfitted (KBP).
Engagement
and
Acquisition
Radars
The
Tunguska/Pantsir
family
of
the
SPAAGMs
has
seen
a
range
of
different
radar
packages
installed
since
the
initial
IOC in 1983. All follow the
model established by the 1960s 9K33 / SA-8 Gecko, with a 360º search
radar for acquisition and coarse tracking, and narrow beam precision
tracking radar on the front of the system turret, used for target and
missile beacon tracking.
The earliest 2K22/2S6 Tunguska variants employed a radar package, which used a 1RL144 search radar with a singly curved cylindrical parabolic section reflector, and a Cassegrain monopulse tracking antenna. This design has been designated the Hot Shot in Western literature. It was supplemented by a 1RL138 IFF interrogator. Russian references list no less than four variants of of the search radar as 1RL144 for the Tunguska, 1RL144M for the Tunguska M, and the 1RL144M-VA/VS.
The progressive iterations in the development of the Pantsir series resulted in a more complex evolution, both in the acquisition and engagement radar components for the new system.
The development of the Pantsir S/S1 saw the introduction, initially, of a search radar with a doubly curved parabolic surface and eliptical shape. This was supplanted in production variants with a VNIIRT developed phased array. The latter design has since appeared on 2K22M1 Tunguska M1 demonstrators, as well as tracked and wheeled 96K6 Pantsir S1 demonstrators and production systems.
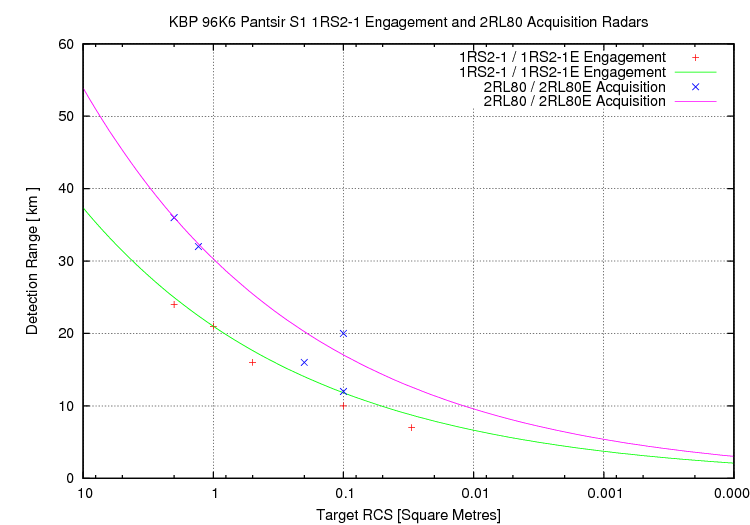
The VNIIRT developed PESA technology acquisition radar on the Pantsir S1, the 2RL80/2RL80E, uses a mechanically rotated 1776 x 940 mm sized 760 kg passive S-band phased array. The design provides elevation coverage between 0° and 60°, range coverage between 1 and 50 km, and performs a circular scan in 2 or 4 seconds. The radar can initiate tracking in 2 seconds. Cited detection range performance for a 1 m2 target is 47 km, for a 0.1 m2 target is 26 km. Cited clutter rejection is 55 dB. Accuracy figures cited are 50 metres in range, 15 - 18 min of arc in azimuth, and 25 - 30 min of arc in elevation.
Elevation coverage is selectable in increments of 0° - 60°, 0° - 30°, 40° - 80° and 0 - 25°, and the radar can search a 360° circle at 15 or 30 RPM. Range coverage can be selected in several modes, at 1-30 km, 1-50 km, 1-25 km and 3-80 km.
Acquisition performance for various target types has also been cited, with notable inconsistencies:
Early Pantsir S1 demonstrators initially used an MMW band monopulse tracking antenna, with a characteristic conical radome, with the Russians claiming two discrete Phazotron designs in this configuration, the 1L36-01 Roman and later 1RS2-E Shlem.
This pulse Doppler radar is designated the 1RS2/1RS2-E Shlem or SSTsR (Stantsiya Slezheniya Tsel'a i Rakety - Target and Missile Tracking Station), initially designated the 1RS1 and 1RS1-E for export. Cited tracking range performance for a 2 m2 target is 30 km. Cited RMS angular errors for X-band operation are 0.3-0.8 milliradians, for Ku-band operation 0.2-0.4 milliradians, with a 5 metre range error.
The X-band component of the SSTsR is used for target tracking, and uplink of missile steering commands., the Ku-band component for target and missile beacon tracking. The system typically guides one or two missile rounds against a single target.
This design has since appeared on the 2K22M1 Tunguska M1 demonstrators, various repackaged Pantsir variants on smaller chassis, usually with the 2RL80E acquisition radar.
In 2004 the requirement for the PVO engagement radar changed, when it was expected that the program would be cancelled. A new requirement was issued to increase the number of concurrent targets to be tracked and engaged, and engagement range was increased. This likely reflects the success of the US GBU-31/32/35/38 JDAM and emergence of analogues globally, where more than two weapons would be released from an aircraft concurrently. With the GBU-39/B Small Diameter Bomb intended to be released eight at a time, the Roman and Shlem would be saturated in a single aircraft attack.
This resulted in the development of an entirely new PESA based radar, curiously designated the 1RS2-1 / 1RS2-1E, but also incorrectly labelled by a Russian source as the 1RL123-E. VNIIRT has been credited with the development of this design. To date all imagery has excluded views of the PESA antenna without the protective radome, so the following description is based on recent public disclosures and is yet to be validated [1][2]:
The primary antenna is used for target and missile tracking, it is supplemented by a command link antenna which is part of the APKNR (Apparatura Peredachi Komand i Naprovadzaniya Raket) subsystem for datalink control of the missiles.
A more detailed discussion can be found under Engagement and
Fire Control Radars.The earliest 2K22/2S6 Tunguska variants employed a radar package, which used a 1RL144 search radar with a singly curved cylindrical parabolic section reflector, and a Cassegrain monopulse tracking antenna. This design has been designated the Hot Shot in Western literature. It was supplemented by a 1RL138 IFF interrogator. Russian references list no less than four variants of of the search radar as 1RL144 for the Tunguska, 1RL144M for the Tunguska M, and the 1RL144M-VA/VS.
The progressive iterations in the development of the Pantsir series resulted in a more complex evolution, both in the acquisition and engagement radar components for the new system.
The development of the Pantsir S/S1 saw the introduction, initially, of a search radar with a doubly curved parabolic surface and eliptical shape. This was supplanted in production variants with a VNIIRT developed phased array. The latter design has since appeared on 2K22M1 Tunguska M1 demonstrators, as well as tracked and wheeled 96K6 Pantsir S1 demonstrators and production systems.
The VNIIRT developed PESA technology acquisition radar on the Pantsir S1, the 2RL80/2RL80E, uses a mechanically rotated 1776 x 940 mm sized 760 kg passive S-band phased array. The design provides elevation coverage between 0° and 60°, range coverage between 1 and 50 km, and performs a circular scan in 2 or 4 seconds. The radar can initiate tracking in 2 seconds. Cited detection range performance for a 1 m2 target is 47 km, for a 0.1 m2 target is 26 km. Cited clutter rejection is 55 dB. Accuracy figures cited are 50 metres in range, 15 - 18 min of arc in azimuth, and 25 - 30 min of arc in elevation.
Elevation coverage is selectable in increments of 0° - 60°, 0° - 30°, 40° - 80° and 0 - 25°, and the radar can search a 360° circle at 15 or 30 RPM. Range coverage can be selected in several modes, at 1-30 km, 1-50 km, 1-25 km and 3-80 km.
Acquisition performance for various target types has also been cited, with notable inconsistencies:
- 36 km for a small fighter with a 2 m2 RCS;
- 20 km for a manoeuvring cruise missile with a 0.1 m2 RCS;
- 16 km for a glidebomb with a 0.2 m2 RCS;
- 12 km for an AGM-88 HARM anti-radiation missile with a 0.1 m2 RCS;
- 32 km for an AH-64 Apache attack helicopter.
Early Pantsir S1 demonstrators initially used an MMW band monopulse tracking antenna, with a characteristic conical radome, with the Russians claiming two discrete Phazotron designs in this configuration, the 1L36-01 Roman and later 1RS2-E Shlem.
This pulse Doppler radar is designated the 1RS2/1RS2-E Shlem or SSTsR (Stantsiya Slezheniya Tsel'a i Rakety - Target and Missile Tracking Station), initially designated the 1RS1 and 1RS1-E for export. Cited tracking range performance for a 2 m2 target is 30 km. Cited RMS angular errors for X-band operation are 0.3-0.8 milliradians, for Ku-band operation 0.2-0.4 milliradians, with a 5 metre range error.
The X-band component of the SSTsR is used for target tracking, and uplink of missile steering commands., the Ku-band component for target and missile beacon tracking. The system typically guides one or two missile rounds against a single target.
This design has since appeared on the 2K22M1 Tunguska M1 demonstrators, various repackaged Pantsir variants on smaller chassis, usually with the 2RL80E acquisition radar.
In 2004 the requirement for the PVO engagement radar changed, when it was expected that the program would be cancelled. A new requirement was issued to increase the number of concurrent targets to be tracked and engaged, and engagement range was increased. This likely reflects the success of the US GBU-31/32/35/38 JDAM and emergence of analogues globally, where more than two weapons would be released from an aircraft concurrently. With the GBU-39/B Small Diameter Bomb intended to be released eight at a time, the Roman and Shlem would be saturated in a single aircraft attack.
This resulted in the development of an entirely new PESA based radar, curiously designated the 1RS2-1 / 1RS2-1E, but also incorrectly labelled by a Russian source as the 1RL123-E. VNIIRT has been credited with the development of this design. To date all imagery has excluded views of the PESA antenna without the protective radome, so the following description is based on recent public disclosures and is yet to be validated [1][2]:
- Operating centre wavelength claimed by KBP to be “8 mm in the K-band” - antenna geometry suggests 15 mm (20 GHz) to 18 mm (16.7 GHz);
- Beamsteering angles of up to ±45° of arc;
- Mechanical PESA boresight steering in elevation between -5° and 82°;
- Track while scan of nine separate targets;
- 90% probability of initial target acquisition within 1 second of coordinate transfer from the 2RL80 with errors of ±2.5° in azimuth, ±2.5° in elevation, ±200 m in range and ±60 metres / sec in radial velocity;
- Tracking errors of 0.2 milliradians in azimuth, 0.3 milliradians in elevation, 5 metres in range and 2 metres / sec in velocity;
- Ability to track airborne targets at velocities between 10 to 1,100 metres / sec;
- Ability to capture 4 missiles after launch;
- Ability to track 3 to 4 outbound missiles at velocities between 30 to 2,100 metres / sec;
- Detection range of 24 km against a 2.0 m2 RCS airborne target; 21 km against a 1 m2 RCS airborne target; 16 km against a 0.5 m2 RCS airborne target; 10 km against a 0.1 m2 RCS airborne target; 7 km against a 0.03 m2 RCS airborne target;
The primary antenna is used for target and missile tracking, it is supplemented by a command link antenna which is part of the APKNR (Apparatura Peredachi Komand i Naprovadzaniya Raket) subsystem for datalink control of the missiles.

In July, 2011, Russian target drone manufacturer ENIKS published an image of a Pantsir S1 system equipped with a new acquisition radar design. The radar is a Janus-faced ESA, evidently intended to generate track outputs at a significantly higher rate than the VNIIRT 2RL80/2RL80E on early production systems for the Russian PVO and export clients. The system is claimed to be for an export client, not disclosed, who may be Middle Eastern given the desert camouflage on the prototype vehicle. A higher tracking rate would provide a better capability to track PGM targets, especially variants of the AGM-88 HARM/AARGM.
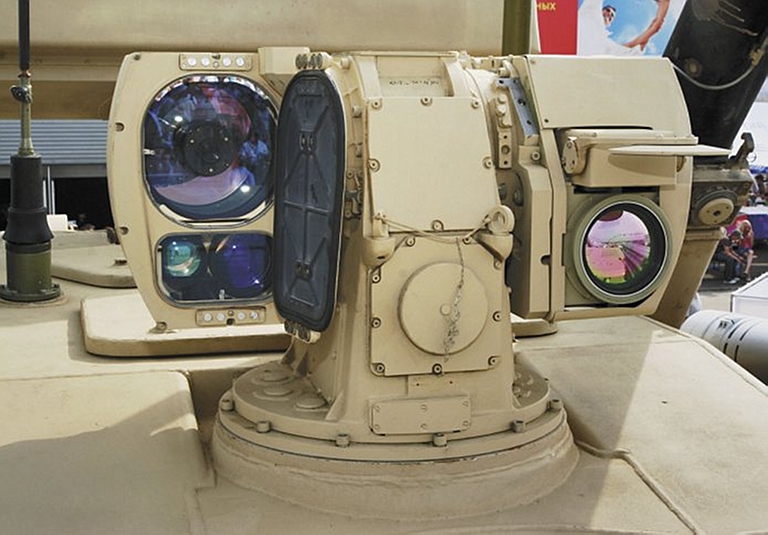

Electro-optical tracking turret on
Pantsir S1. The optics indicate a three field of view stabilised TV
system and a single field of view thermal imaging sensor (image
© Miroslav
Gyűrösi).
Optical Sensors
Early variants of the Tunguska series introduced an electroptical tracker to provide silent angle tracking in jamming environments. The electro-optical tracking system includes a longwave (8 - 14 μm band) thermal imager for target acquisition and tracking, and a dual band short (3 - 5 μm) / midwave (0.6 -1.1. μm) IR tracker for angular measurement of the missile beacon.In the Pantsir S1 the AOP (Avtonomniy Opticheskiy Post) is cued by the radar system, and provides angle tracking of the target and missiles. The cited system specifications are [1][2]:
- Azimuth coverage of ± 90 °;
- Elevation coverage from -5 ° to 82°;
- Angular tracking rate of 100° / sec;
- Angular acceleration of 170° / sec;
- French Sagem MATIS LR midwave thermal imager with WFOV of 4.17° x 6.25°, and NFOV of 0.87° x 1.3°, with a 0.05 mrad angular track error;
- Acquisition performance: F-16 at 17 to 26 km; AGM-88 HARM at 13 to 15 km; cruise missiles at 11 to 14 km, and glidebombs at ~10 km;

 |
||
|
Terminal
stage cutaway: 1 - proximity fuse; 2 - contact fuse; 3 - warhead; 4 -
explosive filler; 5 - canard actuators; 6 - electronics module; 7 -
gyro package; 9 - RF transponder beacon; 10 - optical beacon (Images via KBP, Russkaya Sila, Vestnik
PVO)
|
9M311 and 57E6
Surface to
Air Missiles and 2A38 Gun
The 2K22 / 96K6 / SA-19 / SA-22 systems use variants of one basic
missile and one basic gun design.The missile designs are all derivatives of the two stage command link guided 9M311 weapon. This is a 42 kg launch weight missile, with a low smoke motor intended to avoid problems with optical/infrared tracking of targets and laser rangefinding. The second terminal kill stage is unpowered and relies on kinetic energy imparted by the boost stage, the design strategy intended to minimise the dead weight and drag of the kill stage. Average missile speed is cited at 600 m/s (~Mach 2), and the weapon has a cited capability to engage targets manoevring at 5-7G, although this is not consistent with the cited 18G capability of the missile.
Early variants of the missile use a laser proximity fuse, later variants a radio proximity fuse, with a blast fragmentation warhead. The fuse is triggered ~5 metres from the target. An impact fuse is also provided, with the proximity fuse disabled for shots against surface targets.
The principal differences between the production 57E6 missile, and earlier 9M311 and 9M335, are the use of a larger booster and filament wound composite casings replacing light metal alloys, and the introduction of a larger and more lethal expanding rod warhead. The higher impulse of the propulsion system, and lighter missile structure, result in greater range and velocity compared to the 2K22 / SA-19 missile system.
All missiles are ejected from the launch tube / storage container by a gas generator cartridge, with the booster ignited once the missile has cleared a safe distance. Aerodynamic canard controls are employed for the second stage. Russian sources claim the use of a ram air generator to power the missile electronics, but there is not visible evidence of conventionl vanes for this purpose.
The 57E6 missile weighs 71 kg at launch, of which 20 kg is the warhead section. Booster burn duration is 1.5 seconds, accelerating the missile to 1220 metres/s. The cited velocity profile for the 57E6-E export variant is 900 metres/s at 12 km and 700 metres/s at 18 km range.
The 90 mm diameter expanding rod warhead uses 5 kg of explosive filler, and employs 47 rods of 5 mm diameter and 770 mm length. This is intended to provide a 100 percent probability of hitting a coplanar target at a range of up to 6 metres, and a 65 percent probability of hitting a coplanar target at a range of 9 metres. The warhead is designed to produce ~700 2.8 gram fragments, and ~2,260 0.9 gram fragments. The radar proximity fuse range is cited at 9 metres.
Export 57E6-E missile rounds employ a longer burn duration booster which has raised the peak velocity to 1,300 metres/s. These rounds have a launch weight of 75.7 kg.
Missile rounds for domestic Russian PVO use are designated the 95Ya6 series, with the current block designated the 95Ya6.04. These missiles are cited to have an effective range of 20 km and ceiling of 15 km, making them highly competitive against legacy area defence SAMs.
An improved SAM round for PVO use, believed to be the 23Ya6, is expected to soon be introduced. This weapon would appear to use the same terminal stage as the current 57E6/95Ya6 series, but introduces a longer and larger 210 mm diameter booster stage, versus the 170 mm diameter booster in current rounds. Russian sources suggest an ability to engage targets travelling at 1,850 metres/sec, against 1,000 metres/sec cited for the existing round. With higher kinetic energy the improved missile would reduce engagement times, and provide more G capability for endgame manoeuvres - otherwise a traditional weakness of command link and beam rising SAMs.
The 2A38 series 30 mm gun is a twin barrel revolver design with a belt feed and an electrical drive. The barrels are cooled using water or an anti-freeze fluid. The barrels can be elevated to +85º and depressed to -9º relative to the turret base. Cited total rate of fire for the 2K22 variant of the gun is 4060-4810 rds/min with a muzzle velocity of 960-980 m/sec. A range of shell types are available including tracers, HEI and fragmentation.
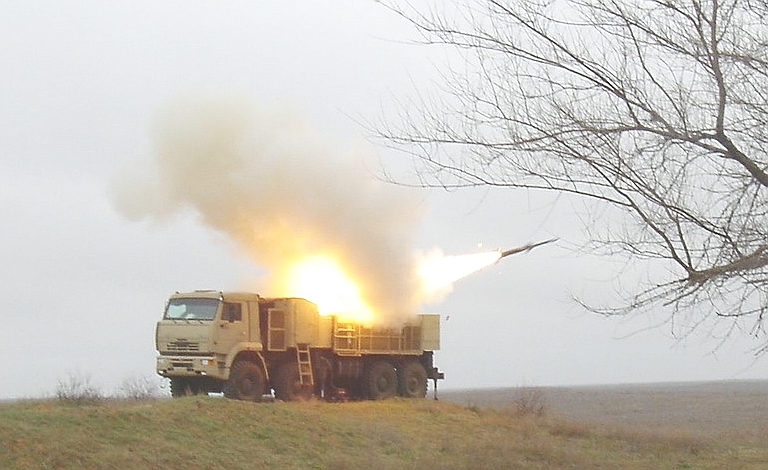

Pantsyr
S1 launching a missile at the Kapustin Yar test range (KBP).
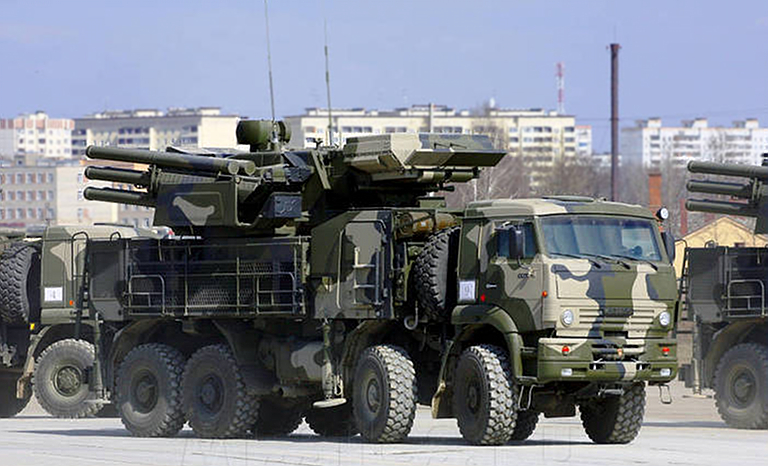

Operational 96K6 Pantsir S1 on parade (© 2010 Evgeniy Yerokhin, Missiles.ru).

Operational 96K6 Pantsir S1 on parade (© 2010 Evgeniy Yerokhin, Missiles.ru).
Production and Exports
Due
to
its
late
deployment
during
the
Cold
War,
the
2K22/2S6
Tunguska
was
never
exported
in
the
vast
quantities seen with the ZSU-23-4. Most
former Soviet 2S6 and 2S6M systems were claimed by Russia, Belarus and
the Ukraine upon the breakup of the USSR. Known export clients include
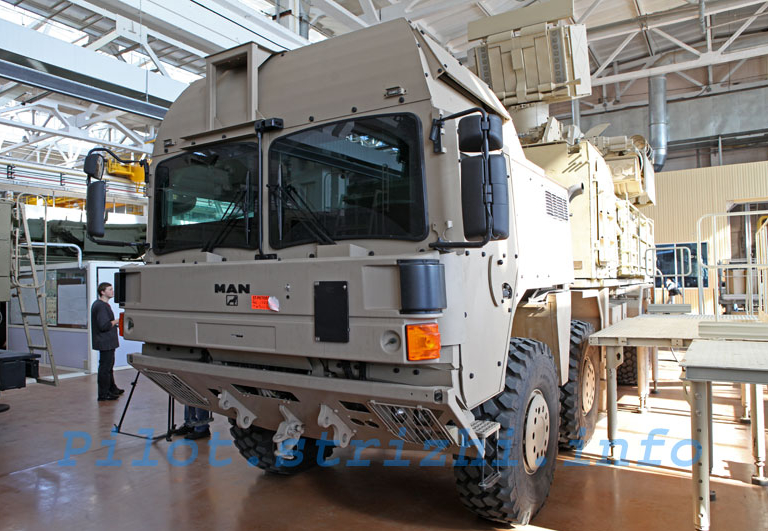
India (M and M1) and Morocco (M1).The Pantsir has been ordered by the UAE, Syria and Algeria, and Iran is also claimed as a client. European sources claim the PLA and Greece were negotiating for the system. The system is offered on the 8 x 8 KAMAZ-6560, a specially stretched 8 x 8 MZKT-7930, the tracked GM 352M1E chassis (with a reduced missile loadout and more basic radar), or an EU sourced MAN SX 45 8 x 8 truck.
At least one prototype Pantsir S1 system has been recently built on the BAZ 6909 “Voshchina” series 8 x 8 chassis, common to the S-300PMU2 / S-400 5P85TE2 TEL, NNIIRT Nebo M radar system, and initially developed as a heavy artillery tractor for offroad use. This 41,300 kg gross weight vehicle is powered by a YaMZ-8431.10-200 or YaMZ-8942.10-033 turbocharged diesel, rated at 347.8 kW/475 SHP. It can climb obstacles of up to 1.4 metres in height, and the 550/75R21 tyres are connected to a central air pressure control system, similar to many armoured vehicles, to maintain inflation when perforated, and control traction in very soft terrain. To date all operational systems with Russian military units have been observed on the KAMAZ-6560. The larger BAZ-6909 would offer better cross country performance and potentially more reload rounds in storage. It is likely this will become the standard production configuration for the Russian PVO.
Russian media reports in 2010 indicated that operational 96K6 / SA-22 batteries were being assigned to protect S-400 / SA-21 strategic SAM system batteries from Precision Guided Munition (PGM) attacks. This is consistent with previously published and planned air defence doctrine.
2K22/96K6 Technical Data
| System/Parameter |
ЗРПК
«Тунгуска» Tunguska SPAAG |
ЗРПК
«Тунгуска-М» Tunguska M SPAAG |
ЗРПК
«Тунгуска-М1» Tunguska M1 SPAAG |
ЗРПК
«Роман» (ранний
«Панцирь») Roman (Early Pantsir) |
ЗРПК
«Панцирь-С1» Pantsir S1 |
| Год принятия на вооружение IOC Year |
1982 |
1990 |
2004 |
Не принят |
В
конце 2007- начале 2008 |
| Ракетное вооружение Missile Armament |
9М311 |
9М311 |
9М311-1М |
9М335 |
57Э6Е |
| Боекомплект, ракет Missile Loadout |
8 |
8 |
8 |
12 |
8-12 |
| Артиллерийское вооружение Gun Armament |
2х2А38
(два 30-мм двухствольных автомата) (two 30 mm twin barrel guns) |
2х2А38М
(два 30-мм двухствольных автомата) (two 30 mm twin barrel guns) |
2х2А38М
(два 30-мм двухствольных автомата) (two 30 mm twin barrel guns) |
2х2А72
(две 30-мм одноствольные пушки) (two 30 mm single barrel guns) |
2х2А38М
(два 30-мм двухствольных автомата) (two 30 mm twin barrel guns) |
| Боекомплект, выстрелы Gun Ammo [rds] |
1936 |
1936 |
1904 |
750 |
1400 |
| Шасси Vehicle Chassis |
Гусеничное
ГМ-352 Tracked GM-352 |
Гусеничное ГМ-352 Tracked GM-352 |
Гусеничное
ГМ-5975 Tracked GM-5975 |
Автомобильное
КамАЗ-7406 или УралАЗ 745.10 Wheeled KamAZ 7406 or UralAZ 745.10 |
Автомобильное
КАМАЗ-6350, МЗКТ, MAN, гусеничное
ГМ-352М1Е Wheeled KAMAZ-6350 MZKT-7930 MAN, Tracked GM-352M1E |
| Зона поражения самолета Engagement Evelope Aircraft Targets |
|||||
| Ракетным вооружением Using Missiles |
|||||
| По дальности Range |
2500-8000 |
2500-8000 |
2500-10000 |
1000-12000 |
1200-20000 |
| По высоте Altitude |
15-3500 |
15-3500 |
15-3500 |
5-8000 |
5-15000 |
| Артиллерийским вооружением Using guns |
|||||
| По дальности Range |
200-4000 |
200-4000 |
200-4000 |
200-4000 |
200-4000 |
| По высоте Altitude |
0-3000 |
0-3000 |
0-3000 |
0-3000 |
0-3000 |
| Темп стрельбы, выстр./мин/ствол Rate of Fire/BBL |
1015 |
1015 |
1250 |
700 |
1250 |
| Число одновременно поражаемых
целей
ракетным оружием Concurrently Engaged Targets by Missile |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
| Table Source: Said Aminov @ Vestnik PVO |
|||||
2K22/96K6 Battery Components
| 2K22/2K22M
Battery
Components |
|||
| System |
Qty |
Function/Composition |
Vehicle |
| 2S6/2S6M |
4-6 |
8
Round
SPAAGM |
GM-352 |
| 2F77M |
2-3 |
8
Round
Missile
Transporter/Transloader |
KamAZ-43101 |
| 9S737MK
Ranzhir PPRU-1M |
1 |
Mobile
Command
Post |
MT-LBu |
| 1R10-1M |
1 |
Engineering
Repair/Test
Station |
Ural-43203-1012 |
| 2F55-1 |
1 |
Missile
Preparation/Assembly
Station |
Ural-43203-1012 |
| 2V110-1 |
1 |
Engineering
Repair
Station |
Ural-43203-1012 |
| 9V921 |
1 |
Engineering Repair/Test Station | GAZ-66 |
| ITO-APG-M1 |
1 |
Mobile
Workshop |
ZiL-131 |
| 96K6 Battery Components1 | |||
| System |
Qty |
Function/Composition |
Vehicle |
| 96K6
Combat
Vehicle |
4-6 |
12
Round
SPAAGM |
KAMAZ
6530 |
| 2F77M |
2-3 |
8
Round
Missile
Transporter/Transloader |
KamAZ-43101 |
| 9S737MK
Ranzhir |
1 |
Mobile
Command
Post |
MZKT
Volat |
| 1R10-1M |
1 |
Engineering
Repair/Test
Station |
Ural-43203-1012 |
| 2F55-1 |
1 |
Missile
Preparation/Assembly
Station |
Ural-43203-1012 |
| 2V110-1 |
1 |
Engineering
Repair
Station |
Ural-43203-1012 |
| 9V921 |
1 |
Engineering Repair/Test Station | GAZ-66 |
| ITO-APG-M1 |
1 |
Mobile
Workshop |
ZiL-131 |
| Battery Support Components | |||
| P-15M/Kasta
2E2 |
1 | UHF-Band Low Level Acquisition Radar | |
| P-15/Kasta
2E1 |
1 | UHF-Band Acquisition Radar | |
| 1
-
Support
vehicle
types
for
the
96K6
Pantsir
S1
have
yet
to
appear
in
public
documents,
reflecting
the 2008 - 2009 IOC of this recent design.
Vehicle types for the 2K22M1 have been listed as a substitute.
Differences will arise in the support systems for the different radar
packages, and some newer truck types may be used. |
|||
96K6 Pantsir S1 72V6 SPAAGM (KAMAZ 6530)

Operational 96K6 systems on parade in Russia, April-May 2011 (© 2011 Vitaliy V. Kuzmin).
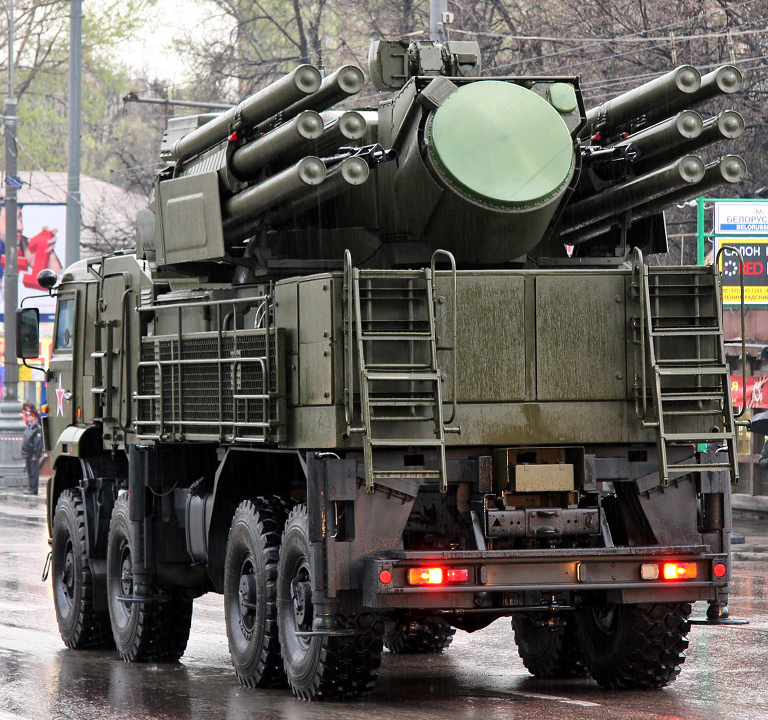

Operational 96K6 systems on parade in Russia, April-May 2011 (© 2011 Vitaliy V. Kuzmin).
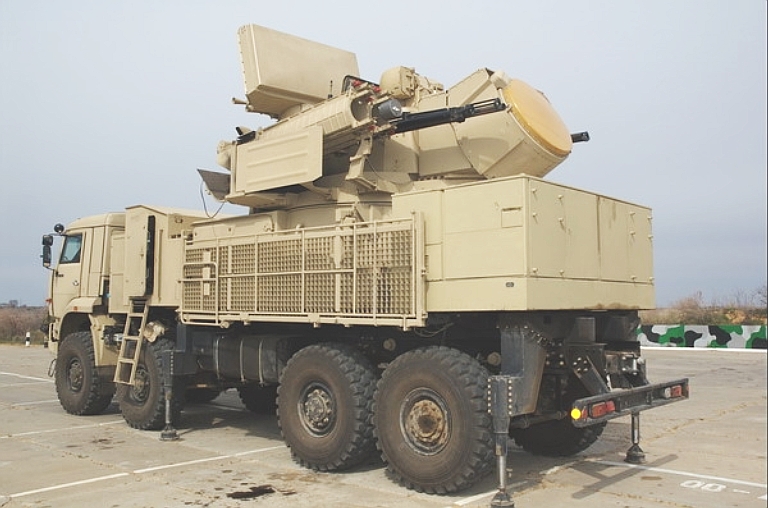

Stowed configuration for transit. The
SA-22 provides very high mobility.
The most recent Pantsir S1 variant has a PESA engagement radar and a
planar array search radar antenna, with much better sidelobe
performance compared to the concave reflective design in the Pantsir S.
This example is painted in desert sand camouflage for demonstration to
Middle Eastern customers - export systems have been supplied on
European MAN chassis.
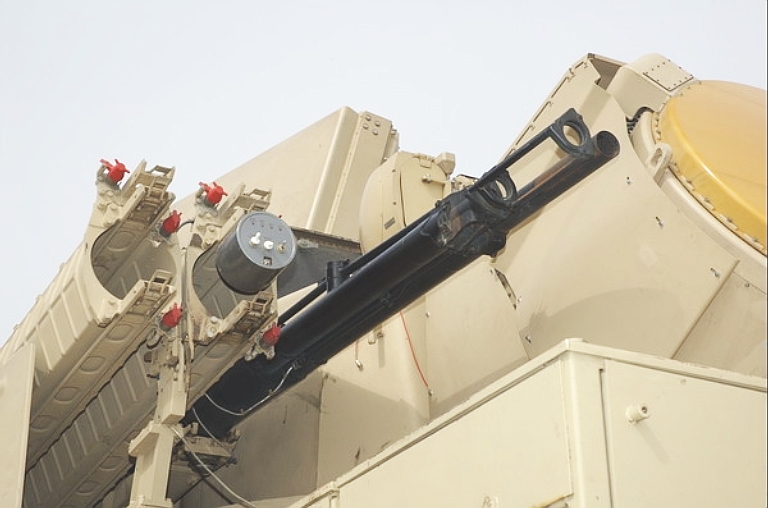

Detail of 30 mm gun system, derived from the GSh-30 aircraft cannon.
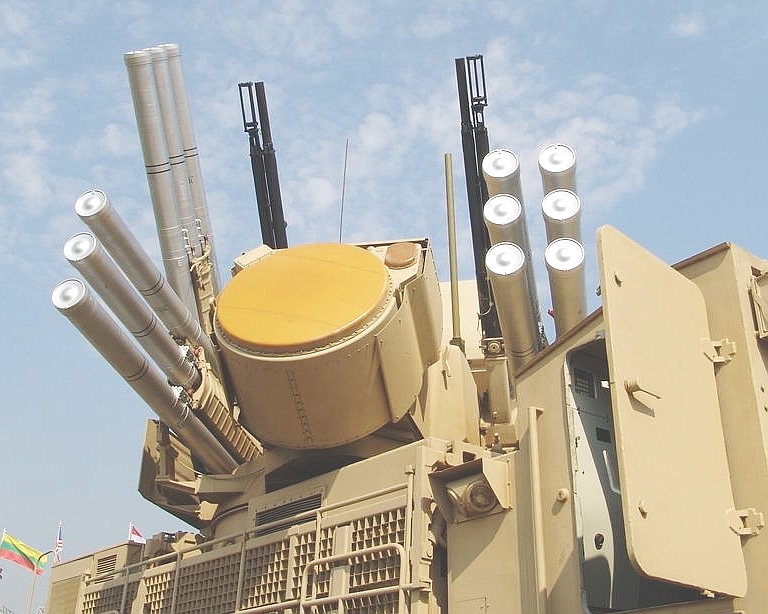

Detail
of new Pantsir S1 Phazotron
X-band phased array engagement radar.
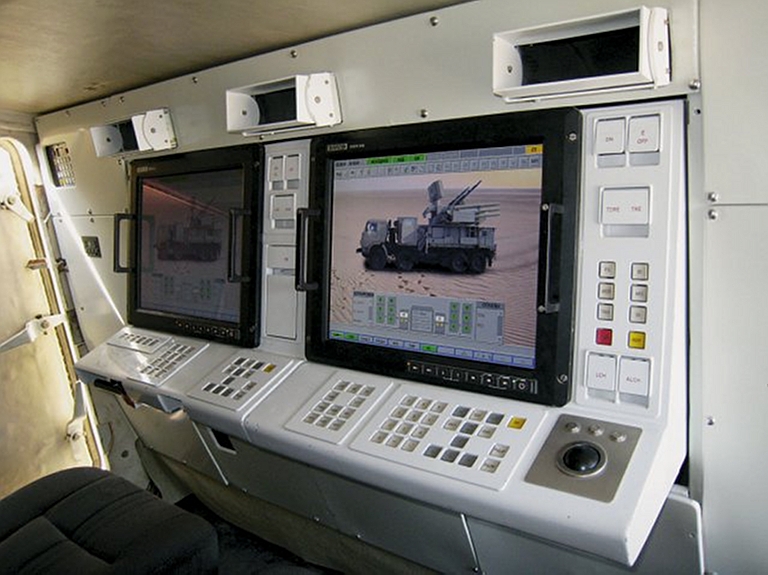

Crew stations in the recent Pantsir S1E configuration (image © Miroslav Gyűrösi).

Crew stations in the recent Pantsir S1E configuration (image © Miroslav Gyűrösi).
96K6 Pantsir S1 72V6 SPAAGM (MAN Cat SX 45)
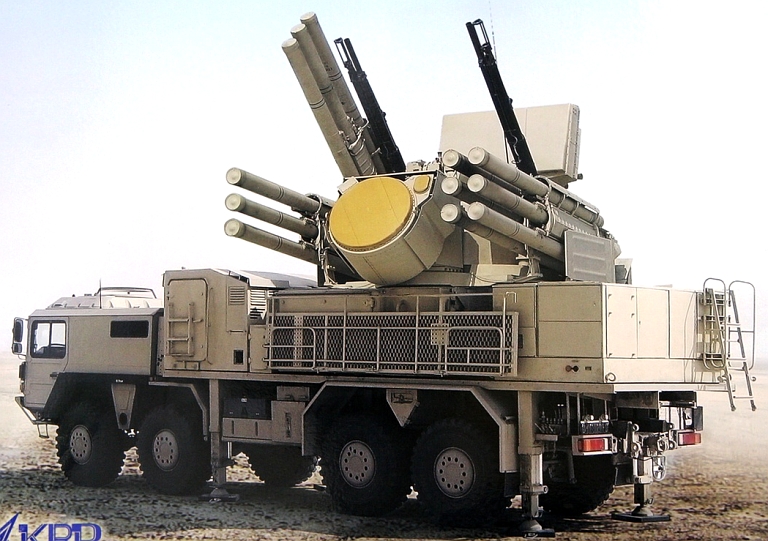

Pantsir
S1E
exported
to
the
UAE
on
a
MAN
Cat
SX
A1
8
x
8
chassis
(Sergei
Kuznetsov
via
Strizhi.ru).
96K6 Pantsir S1 72V6 SPAAGM (BAZ 6909)

Fully deployed 72V6 SPAAGM prototype on BAZ-6909 chassis (Sergei Kuznetsov via Strizhi.ru).
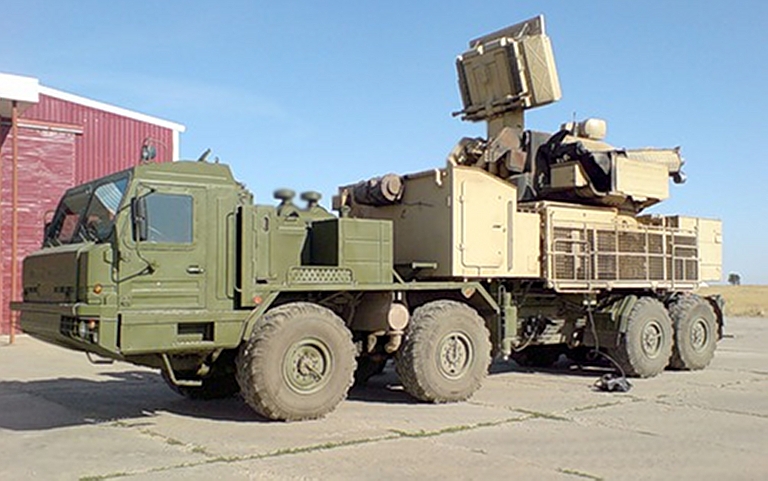

Partly
deployed
72V6
SPAAGM
prototype
on
BAZ-6909
chassis.
The
system
components
are
in
original
production
colours
(Sergei Kuznetsov
via Strizhi.ru).

96K6 Pantsir S1 72V6 SPAAGM (MZKT-7930)
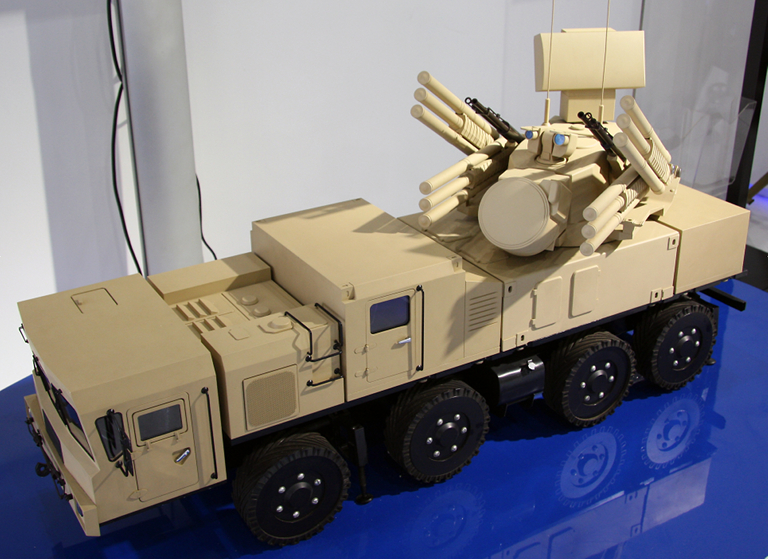

The Belarus built MZKT-7930
continues to be offered as the host platform for the 96K6 Pantsir S1
SPAAGM, as evidenced by this display model at a 2009 arms display (© 2009, Vitaliy
Kuzmin).
The
Pantsir S1 weapon system is being offered as a new build substitute for
the less capable 2K22M1/2S6M1 Tunguska
M/M1 SPAAGM, hosted on the GM-352M1/M1E tracked chassis. This design is
essentially a hybrid of components, mixing the earlier 1RS2-1/1E
engagement radar, the 2RL80E acquisition radar, and a
reduced 8 round payload of the 57E6 -E missile (via Russian Internet).

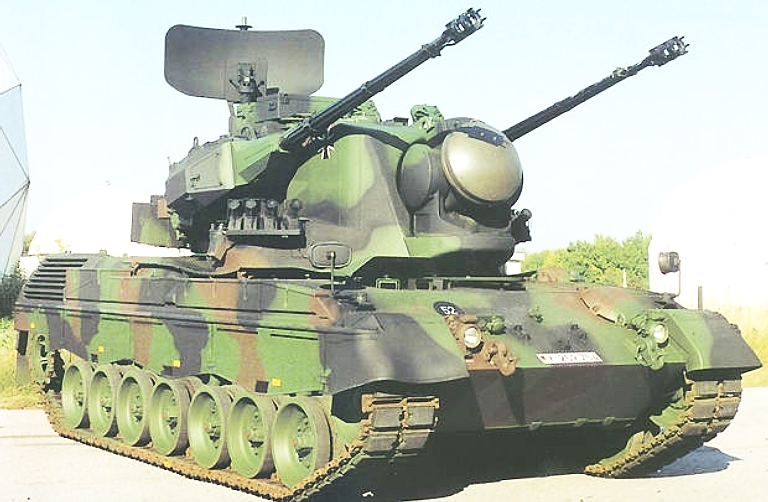
2K22M1/2S6M1 Tunguska M/M1 SPAAGM
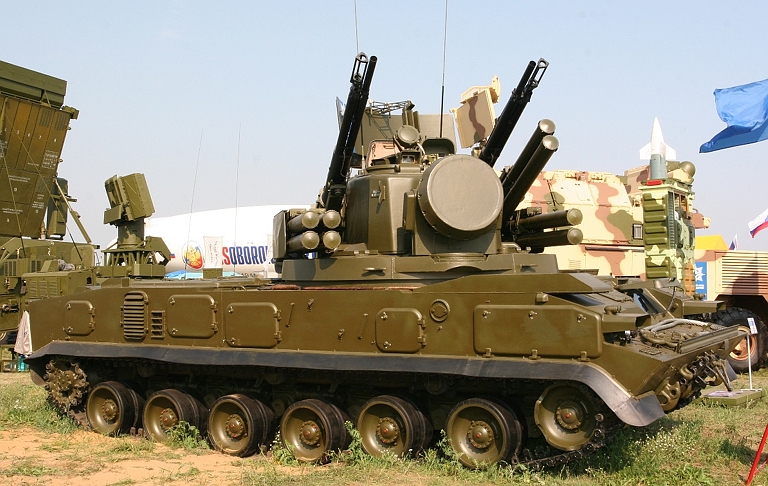

Early configuration
2S6M1
Tunguska M1 system,
note the Hot Shot radar system with the cylindrical paraboloid
section search
antenna and gimballed monopulse tracking antenna (© Miroslav
Gyűrösi).
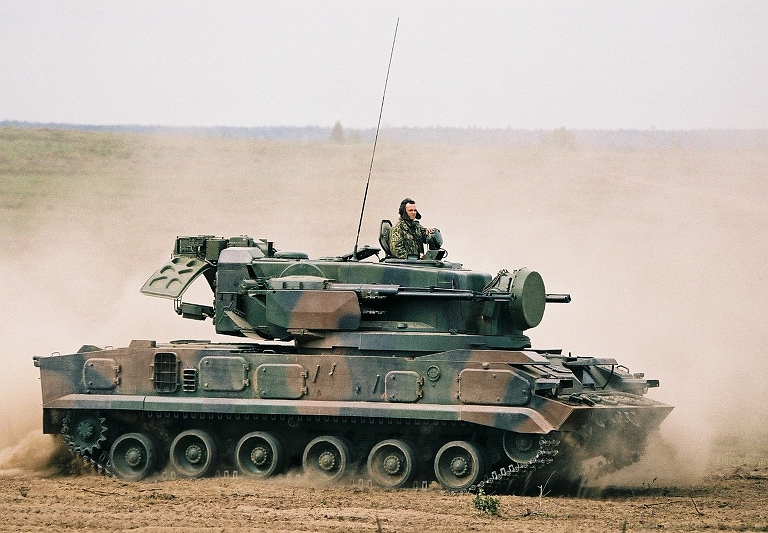
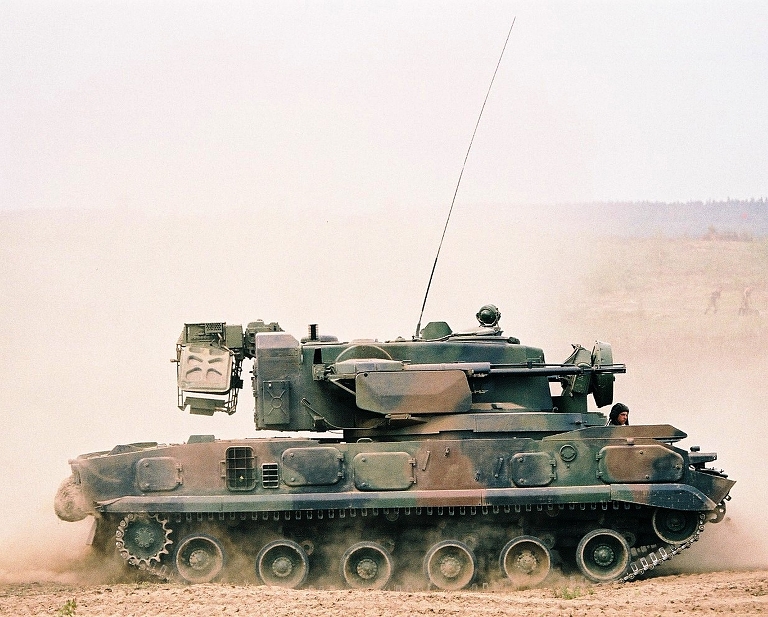
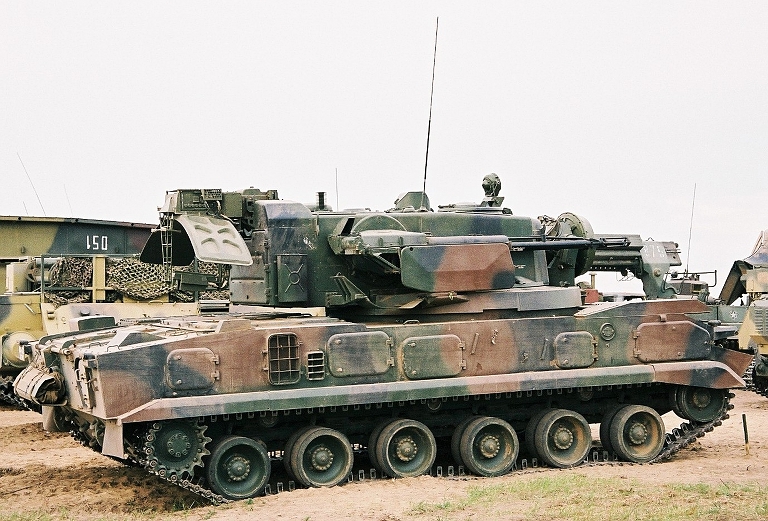




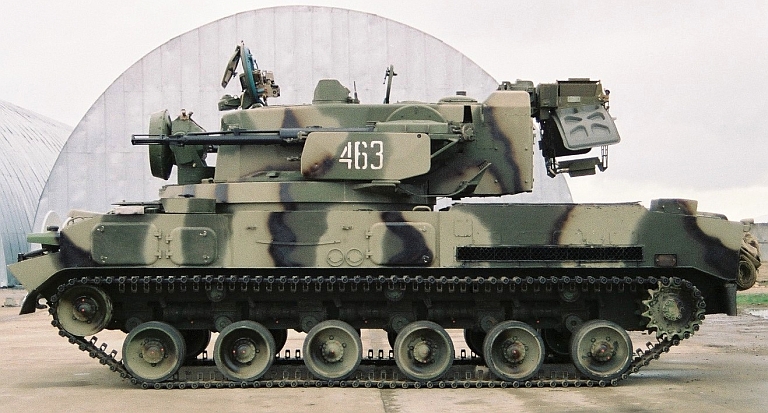
2S6M Tunguska M at the Berezina 2002
exercise. The system is stowed and no missiles are loaded (© Miroslav
Gyűrösi).


2F77M Transporter/Transloader
9S737/MP-22 Ranzhir E Battery Mobile Command Post

The Ranzhir E/M is available in a
lower cost truck variant, intended for applications where high road
mobility is important. For instance a wheeled Pantsir S1 battery would
use the wheeled variant to match the high road speed of the SPAAGMs
(Agat).
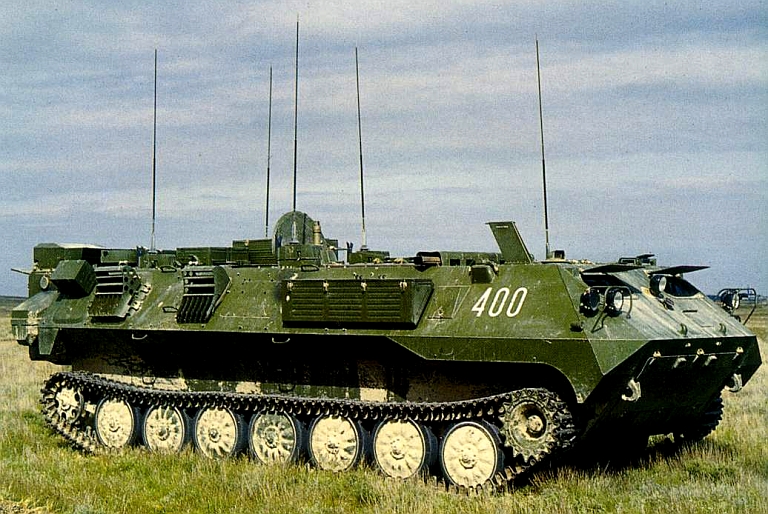

The tracked variant of the Ranzhir series is based on a modified MT-LBu chassis and is typically used with the 2S6M Tunguska.

The tracked variant of the Ranzhir series is based on a modified MT-LBu chassis and is typically used with the 2S6M Tunguska.
51U6/39N6E Kasta 2E1 / 2E2 Flat Face / Squat Eye Acquisition Radar
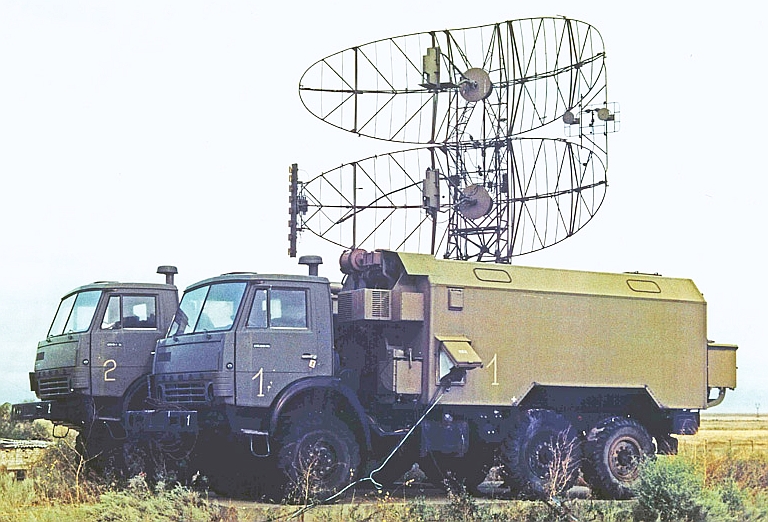

Kasta 2E1 Flat Face E UHF Band Acquisition
Radar. This is a modern digital replacement for the P-19 Flat Face.
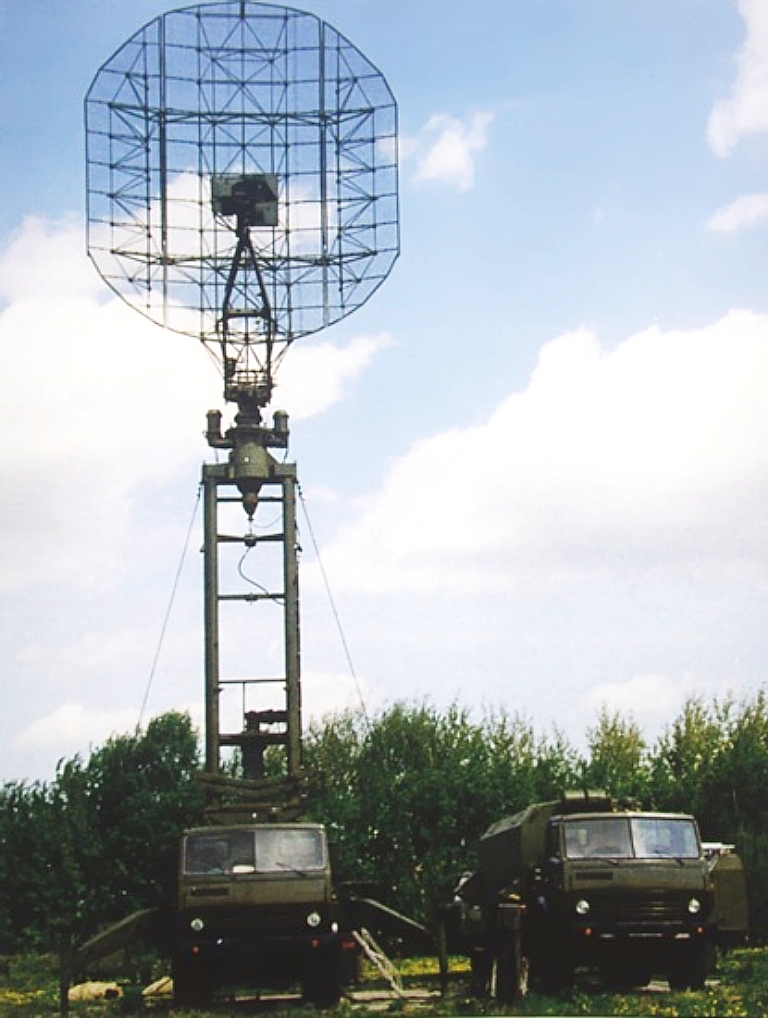

Kasta 2E2 Squat Eye E deployed.
References/Sources:
- Miroslav Gyűrösi, Hybrydowy zestaw przeciwlotniczy Pancyr-S1 Cz.1, NTW - Technika Wojskowa, 6/2010.
- Miroslav Gyűrösi, Hybrydowy zestaw przeciwlotniczy Pancyr-S1 Cz.2, NTW - Technika Wojskowa, 8/2010.
- Said Aminov, Vestnik
PVO, URL: http://pvo.guns.ru; http://pvo.guns.ru/panzir/1rs2e.htm
- Pantsir-S1 Air Defense Missile/Gun System, KBP Instrument Design Bureau, 59 Shcheglovskaya Zaseka St., 300001 Tula, Russia.
- Tunguska-M1 Air Defense Missile/Gun System, KBP Instrument Design Bureau, 59 Shcheglovskaya Zaseka St., 300001 Tula, Russia.
- 30 mm 2A38M Automatic Anti-Aircraft Gun, KBP Instrument Design Bureau, 59 Shcheglovskaya Zaseka St., 300001 Tula, Russia.
- Phazotron Shlem air defence radar system, Phazotron NIIR.
- Martin Rosenkranz, MAKS 2007 Spezial: Pantsir-S1 (SA-22), Russlands neuestes Flugabwehrsystem.
Technical Report APA-TR-2009-0703
|
|||||||||||||
![Sukhoi PAK-FA and Flanker Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/flanker.png) |
![F-35 Joint Strike Fighter Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/jsf.png) |
![Weapons Technology Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/weps.png) |
![News and Media Related Material Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/media.png) |
||||||||||
![Surface to Air Missile Systems / Integrated Air Defence Systems Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/sams-iads.png) |
![Ballistic Missiles and Missile Defence Page [Click for more ...]](APA/msls-bmd.png) |
![Air Power and National Military Strategy Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/strategy.png) |
![Military Aviation Historical Topics Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/history.png)
|
![Information Warfare / Operations and Electronic Warfare Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/iw.png) |
![Systems and Basic Technology Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/technology.png) |
![Related Links Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/links.png) |
|||||||
![Homepage of Australia's First Online Journal Covering Air Power Issues (ISSN 1832-2433) [Click for more ...]](APA/apa-analyses.png) |
|||||||||||||
| Artwork, graphic design, layout and text © 2004 - 2014 Carlo Kopp; Text © 2004 - 2014 Peter Goon; All rights reserved. Recommended browsers. Contact webmaster. Site navigation hints. Current hot topics. | |||||||||||||
|
Site Update
Status:
$Revision: 1.753 $
Site History: Notices
and
Updates / NLA Pandora Archive
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
Tweet | Follow @APA_Updates | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
![F-111 Aardvark Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/f-111.png)
![F/A-18 Hornet and Super Hornet Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/fa-18a.png)
![Aerial Refuelling and Airlift Capabilities Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/aar-lift.png)
![Directed Energy Weapons and Electromagnetic Bombs Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/dew.png)
![Notices and Updates Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/notices-128.png)
![APA NOTAM and Media Release Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/notams-128.png)
![APA Research Activities and Policy / Technical Reports Index [Click for more ...]](APA/research-128.png)
![Search Air Power Australia Website [Click for more ...]](APA/search-128.png)
![Briefings and Submissions - Air Power Australia [Click for more ...]](APA/briefs-128.png)
![Air Power Australia Contacts [Click for more ...]](APA/contacts-128.png)
![Funding Air Power Australia [Click for more ...]](APA/funding-258.png)








